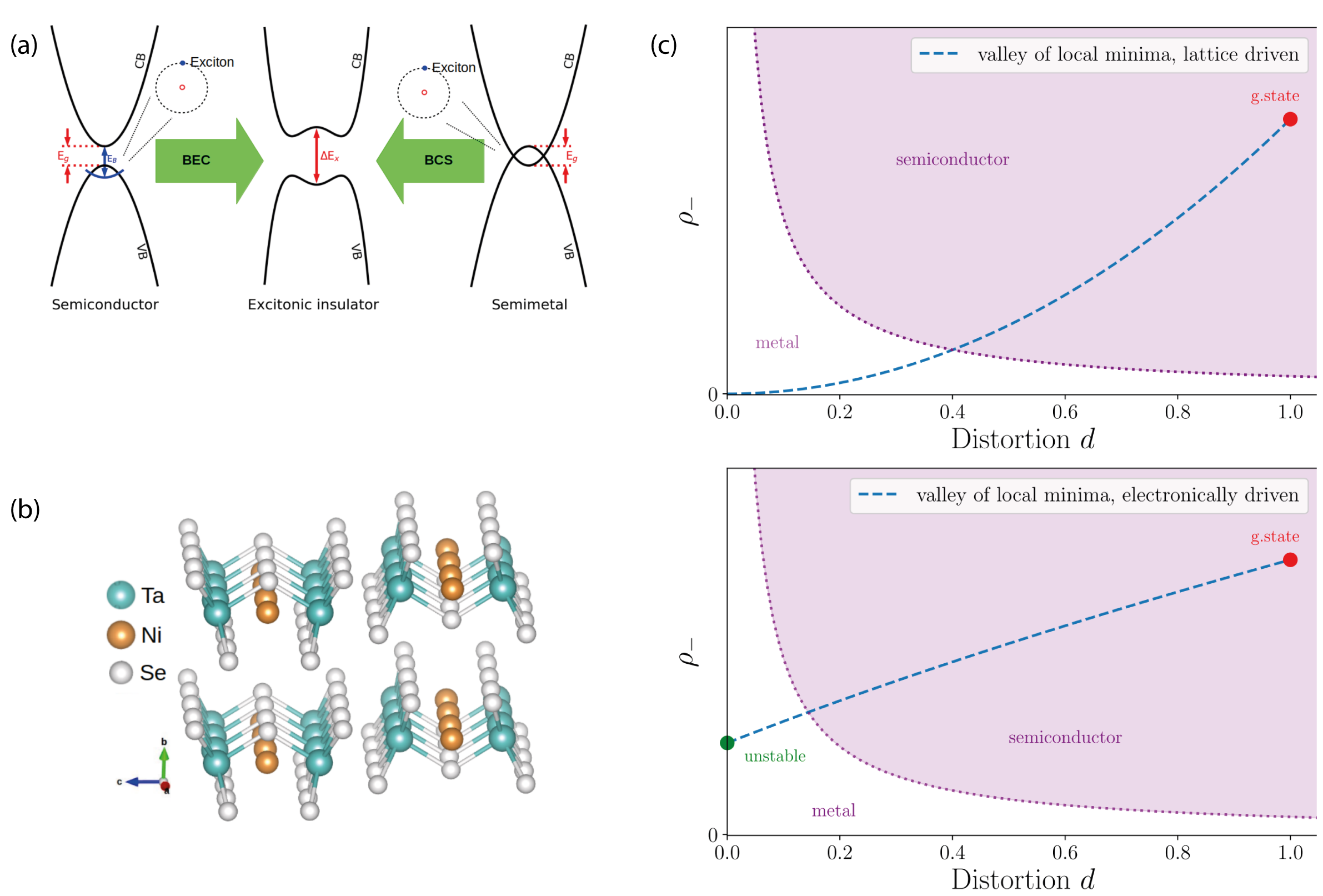
A Quantum material is a material whose properties cannot be interpreted in terms of semi-classical particles. The behaviour of quantum material instead emerges because of the of the collective behaviour of the consituent quasi-particles. An excitonic insulator, a quantum phase consisting of a macroscopic number of electron-hole pairs at equilibrium, is an elusive example of a quantum material and as such has been drawing tremendous attention in the condensed matter community. In our group we have in particular focused on the existance of such a phase in one of the most promising candidate host materials, Ta2NiSe5 (TNSe). TNSe is debated as one of the prime candidates hosting an excitonic insulating groundstate, while it is agreed that its sister material Ta2NiS5 (TNS) undergoes a purely structural phase transition. The debate in the literature is based on controversial interpretation of ARPES and Raman data, which is based on excitonic instabilities [1]. We have shown that the origin of the phase transition in TNSe and TNS have a common structural origin and the main experimental findings are explained by a phononic instability [2,3]. Furthermore we demonstrate a strong THz reflectivity amplification in TNSe upon optical pumping [4].
Ab-initio calculations show that the debatable excitonic phase transition is structural in nature. Adapted from [2].
References:
[1] Nature of Symmetry Breaking at the Excitonic Insulator Transition: Ta2NiSe5
G. Mazza, M. Rösner, L. Windgätter, S. Latini, H. Hübener, A.J. Millis, A. Rubio, A. Georges
Phys. Rev. Lett. 124, 197601 (2020).
DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.124.197601
[2] Common microscopic origin of the phase transitions in Ta2NiS5 and the excitonic insulator candidate Ta2NiSe5.
L. Windgätter, M. Rösner, G. Mazza, and H. Hübener, A. Georges, A.J. Millis, S. Latini, A. Rubio
npj Computational Materials vol 7, num 210 (2021).
DOI: 10.1038/s41524-021-00675-6
[3] The spontaneous symmetry breaking in Ta2NiSe5 is structural in nature.
E. Baldini, A. Zong, D. Choi, C. Lee, M.H. Michael, L. Windgaetter, I.I. Mazin, S. Latini, D. Azoury, B. Lv, A. Kogar, Y. Wang, Y. Lu, T. Takayama, H. Takagi, A.J. Millis, A. Rubio, E. Demler, N. Gedik
arXiv preprint (2020).
DOI: arXiv:2007.02909
[4] Fresnel-Floquet theory of light-induced terahertz reflectivity amplification in Ta2NiSe5.
M. Michael, S.R.U. Haque, L. Windgaetter, S. Latini, Y. Zhang, A. Rubio, R.D. Averitt, E. Demler.
arXiv preprint (2022).
DOI: arXiv:2207.08851